is diabetic ketoacidosis type 1 or 2 Diabetic ketoacidosis (dka) definition, symptoms, diagnosis, treatement
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a severe complication of diabetes mellitus that requires immediate medical attention. This condition occurs when the body cannot produce enough insulin, or when the insulin being produced is not being utilized efficiently by the body. This leads to high levels of glucose in the blood, which the body will try to eliminate through urine. In the process, the body will start breaking down fat for energy, leading to the buildup of ketones in the blood. The accumulation of ketones leads to acidosis, a condition in which the blood becomes too acidic, and can cause serious and life-threatening complications. Symptoms of DKA generally develop gradually over a period of several hours or days. Initially, people with DKA may experience increasing thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue. As the condition progresses, other symptoms may develop, such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, shortness of breath, and confusion. In severe cases, DKA can lead to unconsciousness and even death. Diagnosis of DKA typically involves a combination of blood tests and physical exams. Blood tests will measure glucose, electrolyte, and ketone levels, while physical exams may reveal signs of dehydration, abdominal pain, and respiratory distress. Treatment generally involves hospitalization, intravenous fluids and electrolytes, insulin therapy, and close monitoring of blood glucose and electrolyte levels. In addition, underlying infections or other contributing factors should be identified and addressed. It is important for people with diabetes to recognize the signs and symptoms of DKA and seek medical attention immediately if they experience any of these symptoms. Additionally, people with diabetes should work with their healthcare providers to establish effective diabetes management plans, including regular blood glucose monitoring, medication management, and lifestyle modifications, such as dietary improvements and regular exercise. In summary, DKA is a serious and potentially life-threatening complication of diabetes mellitus. Early recognition and treatment are critical for a successful outcome. People with diabetes should work closely with their healthcare providers to establish effective diabetes management plans and seek medical attention immediately if they experience any symptoms of DKA.
If you are looking for Why Does Diabetic Ketoacidosis Cause Dehydration — DiabetesCareTalk.net you’ve came to the right place. We have 5 Images about Why Does Diabetic Ketoacidosis Cause Dehydration — DiabetesCareTalk.net like Diabetes mellitus type 1, type 2 & diabetic ketoacidosis DKA causes, Pathophysiology Of Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Diabetic ketoacidosis is an and also Why Does Diabetic Ketoacidosis Cause Dehydration — DiabetesCareTalk.net. Read more:
Why Does Diabetic Ketoacidosis Cause Dehydration — DiabetesCareTalk.net
 www.diabetescaretalk.netketoacidosis diabetic dka pathophysiology dehydration acidosis hyperglycemia mellitus hypoglycemia diabetestalk metabolic disambiguation hyperglycemic hyperosmolar
www.diabetescaretalk.netketoacidosis diabetic dka pathophysiology dehydration acidosis hyperglycemia mellitus hypoglycemia diabetestalk metabolic disambiguation hyperglycemic hyperosmolar
Diabetes Mellitus Type 1, Type 2 & Diabetic Ketoacidosis DKA Causes
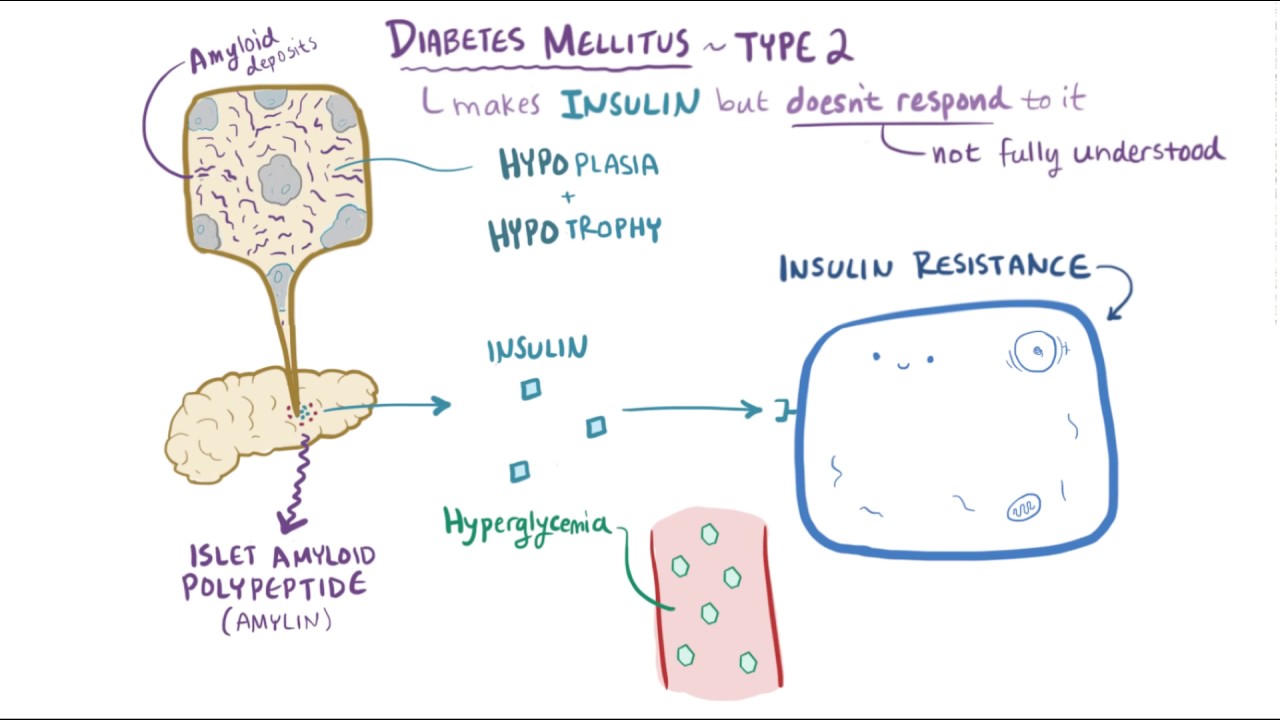 www.youtube.comdiabetes type ketoacidosis dka diabetic causes mellitus symptoms
www.youtube.comdiabetes type ketoacidosis dka diabetic causes mellitus symptoms
Pin By Stoli On EMS | Diabetic Ketoacidosis, Diabetes Education, Nurse
 www.pinterest.comdiabetic ketoacidosis dka ketosis mellitus
www.pinterest.comdiabetic ketoacidosis dka ketosis mellitus
Pathophysiology Of Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Diabetic Ketoacidosis Is An
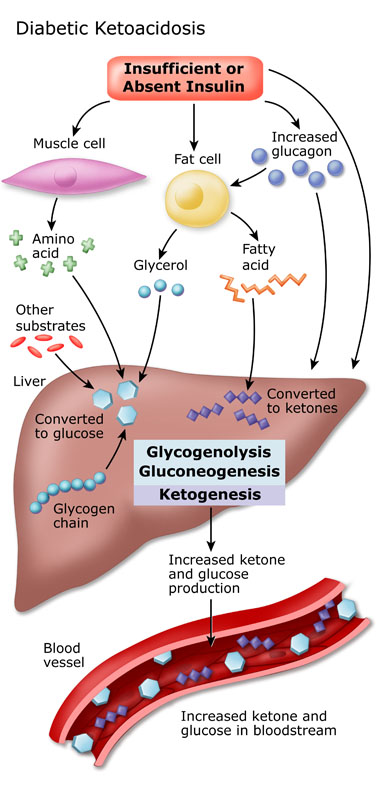 ariadnehopkins.blogspot.comdiabetes ketoacidosis dka diabética aceite insulin cetoacidosis diabetica pathophysiology ucsf complication alzheimer stepwards ketones acidosis blood luchar dtc aceitedecoco rev1
ariadnehopkins.blogspot.comdiabetes ketoacidosis dka diabética aceite insulin cetoacidosis diabetica pathophysiology ucsf complication alzheimer stepwards ketones acidosis blood luchar dtc aceitedecoco rev1
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Definition, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatement
 www.med2date.comketoacidosis diabetes dka diabetic type ketones blood understanding definition symptoms pathophysiology ketogenic diet complications keytones live risks sugar everyone should
www.med2date.comketoacidosis diabetes dka diabetic type ketones blood understanding definition symptoms pathophysiology ketogenic diet complications keytones live risks sugar everyone should
Diabetes type ketoacidosis dka diabetic causes mellitus symptoms. Pathophysiology of diabetic ketoacidosis. Ketoacidosis diabetes dka diabetic type ketones blood understanding definition symptoms pathophysiology ketogenic diet complications keytones live risks sugar everyone should